MODULE ten short answer questions.
saq 1.
A 32 year old male presents with the ambulance service after falling off a dirt bike. His vital signs on arrival are:
HR 112 /min
BP 105/67 mmHg
RR 30 /min
Sats 93% 2L O2
T 36.5 oC
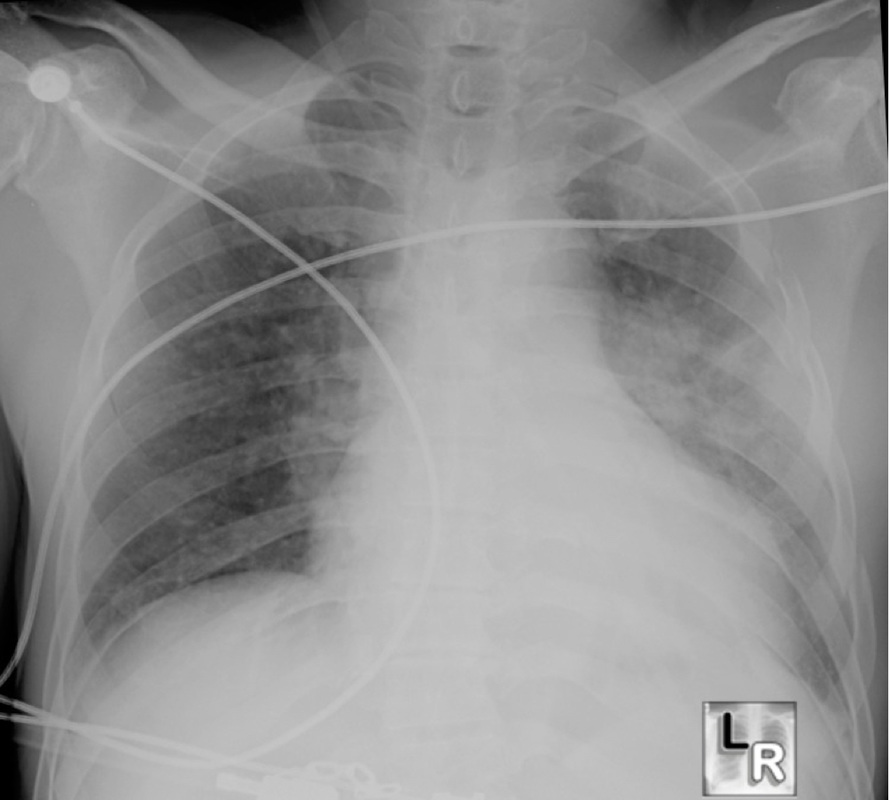
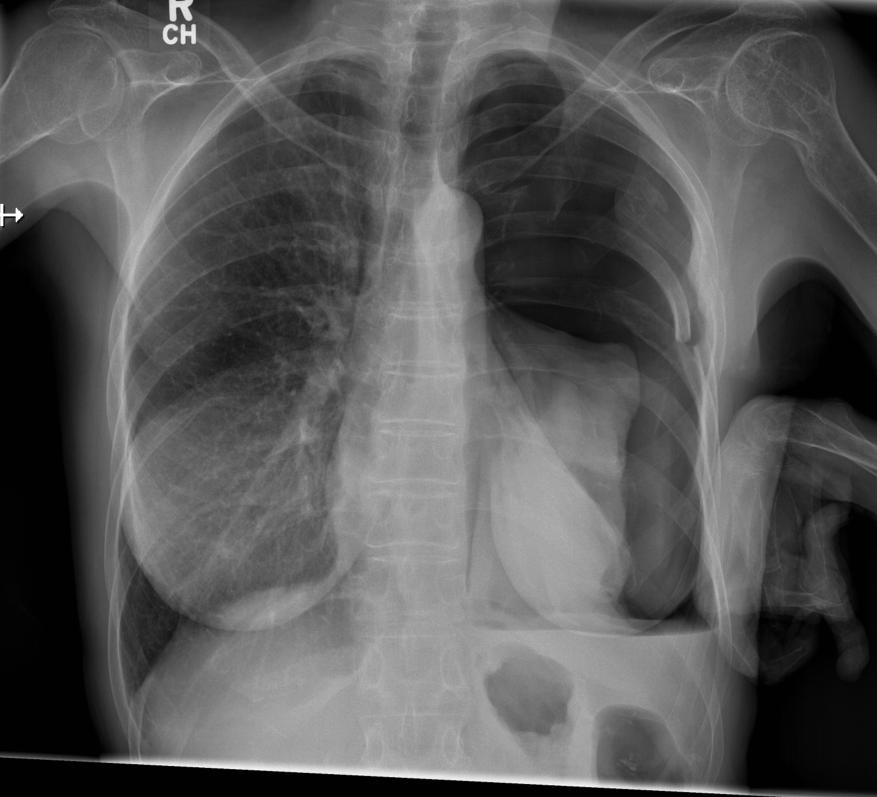
A supine film from the trauma bay is shown below.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 2 positive findings and 2 negative findings from the chest X-ray.
HR 112 /min
BP 105/67 mmHg
RR 30 /min
Sats 93% 2L O2
T 36.5 oC
A supine film from the trauma bay is shown below.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 2 positive findings and 2 negative findings from the chest X-ray.
Question 2. (6 marks)
Describe 3 modality options for managing this patient’s pain.
Question 3. (4 marks)
An arterial blood gas is performed on the patient.
i) Give 2 acid base disorders present. (2 marks)
ii) Perform a calculation to describe the patient's respiratory function (2 marks)
FiO2 .40
pH 7.22
pCO2 58 mmHg
PO2 99 mmHg
HCO3- 19 mmol/L
Na+ 140 mmol/L
K+ 5.5 mmol/L
Cl- 104 mmol/L
Question 4. (4 marks)
On full work up it appears the chest injuries seen above are the only major ones sustained. What are the implications of the patient’s injuries, and where will you refer the patient?
Describe 3 modality options for managing this patient’s pain.
Question 3. (4 marks)
An arterial blood gas is performed on the patient.
i) Give 2 acid base disorders present. (2 marks)
ii) Perform a calculation to describe the patient's respiratory function (2 marks)
FiO2 .40
pH 7.22
pCO2 58 mmHg
PO2 99 mmHg
HCO3- 19 mmol/L
Na+ 140 mmol/L
K+ 5.5 mmol/L
Cl- 104 mmol/L
Question 4. (4 marks)
On full work up it appears the chest injuries seen above are the only major ones sustained. What are the implications of the patient’s injuries, and where will you refer the patient?
saq 2.
A 28 year old male presents to your department after being run over by a motorcycle whilst participating in motocross. The motorcycle ran directly over the patient’s abdomen, and he has tyre marks and a large bruise in the left hypochondrium.
The patient’s initial vital signs are:
HR 105 /min
BP 104/68 mmHg
RR 19 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 36.8 oC
Question 1. (3 marks)
The junior surgical registrar who has attended your trauma call asks you to perform a FAST scan “to exclude abdominal injury”. What is the role of FAST scanning in this patient?
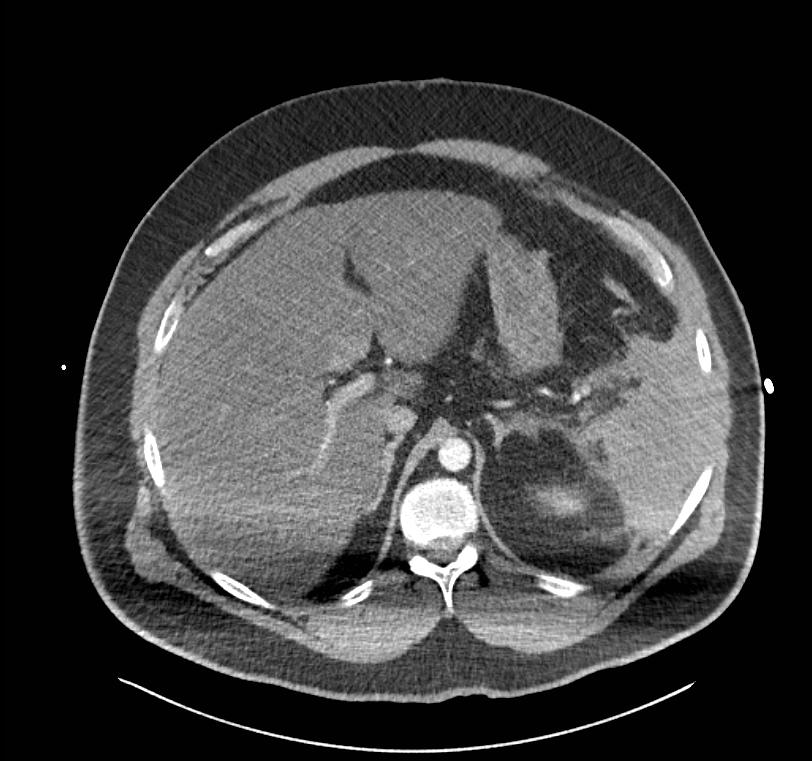
Question 2.
A CT scan of the patient’s abdomen is shown below. What abnormalities does it show? (3 marks)
The patient’s initial vital signs are:
HR 105 /min
BP 104/68 mmHg
RR 19 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 36.8 oC
Question 1. (3 marks)
The junior surgical registrar who has attended your trauma call asks you to perform a FAST scan “to exclude abdominal injury”. What is the role of FAST scanning in this patient?
Question 2.
A CT scan of the patient’s abdomen is shown below. What abnormalities does it show? (3 marks)
Question 3. (4 marks)
The patient’s blood pressure drops on return from CT to 65/-, and the HR increases to 120/min. The patient has already had 2 units of packed red cells in the CT scanning room. There are no other injuries discovered on the CT scan.
What treatments will you administer to this patient in view of this problem?
Question 4. (3 marks)
Give 3 haemodynamic endpoints for these treatments.
The patient’s blood pressure drops on return from CT to 65/-, and the HR increases to 120/min. The patient has already had 2 units of packed red cells in the CT scanning room. There are no other injuries discovered on the CT scan.
What treatments will you administer to this patient in view of this problem?
Question 4. (3 marks)
Give 3 haemodynamic endpoints for these treatments.
saq 3.
A 50 year old woman presents after a domestic altercation. Her partner has stabbed her in the left side of the neck with a kitchen knife.
Question 1. (6 marks)
What are the anatomic boundaries of the zones of the neck?
Question 2. (2 marks)
The stab wound is anterior to the left sternocleidomastoid muscle and above the cricoid cartilage. What are the 2 major vascular structures at risk here?
Question 3.
Give 4 features on examination would indicate injury to one of these two structures. (4 marks)
Question 4. (4 marks)
What are the underlying principles of the “no zone” approach to neck trauma?
Question 1. (6 marks)
What are the anatomic boundaries of the zones of the neck?
Question 2. (2 marks)
The stab wound is anterior to the left sternocleidomastoid muscle and above the cricoid cartilage. What are the 2 major vascular structures at risk here?
Question 3.
Give 4 features on examination would indicate injury to one of these two structures. (4 marks)
Question 4. (4 marks)
What are the underlying principles of the “no zone” approach to neck trauma?
saq 4.
A 38 year old male construction worker presents to the emergency department after an industrial accident. He was hit in the abdomen by a large iron girder swinging from a chain on a crane.
His vital signs on arrival are:
HR 114 /min
BP 88/45 mmHg
RR 28 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 34.2 oC
Question 1. (4 Marks)
Your resus team is unable to site a line in the patient’s cubital fossae or other sites in the arms. Where and by what method will you establish your vascular access? Justify your choice.
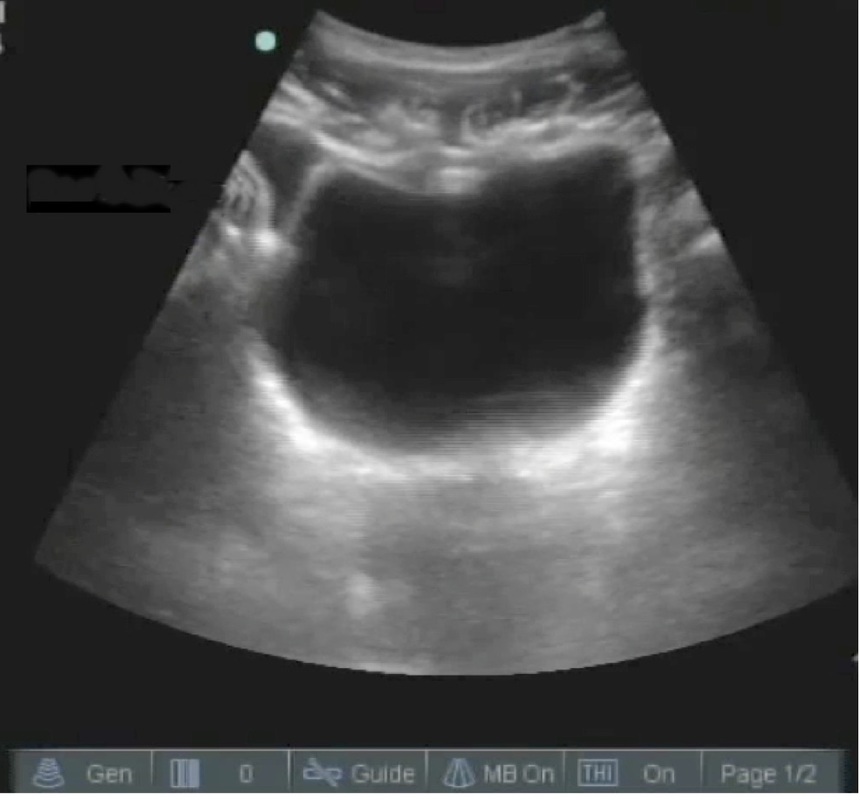
Question 2. (2 marks)
The patient receives 2 units of packed cells and the blood pressure improves to 95/55 and the HR decreases to 105/min. Your registrar performs a bedside ultrasound and a picture is shown below. What does it show, and what are the implications?
His vital signs on arrival are:
HR 114 /min
BP 88/45 mmHg
RR 28 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 34.2 oC
Question 1. (4 Marks)
Your resus team is unable to site a line in the patient’s cubital fossae or other sites in the arms. Where and by what method will you establish your vascular access? Justify your choice.
Question 2. (2 marks)
The patient receives 2 units of packed cells and the blood pressure improves to 95/55 and the HR decreases to 105/min. Your registrar performs a bedside ultrasound and a picture is shown below. What does it show, and what are the implications?
Question 3.
Will you perform a CT scan of the patient? Justify your choice. (2 marks)
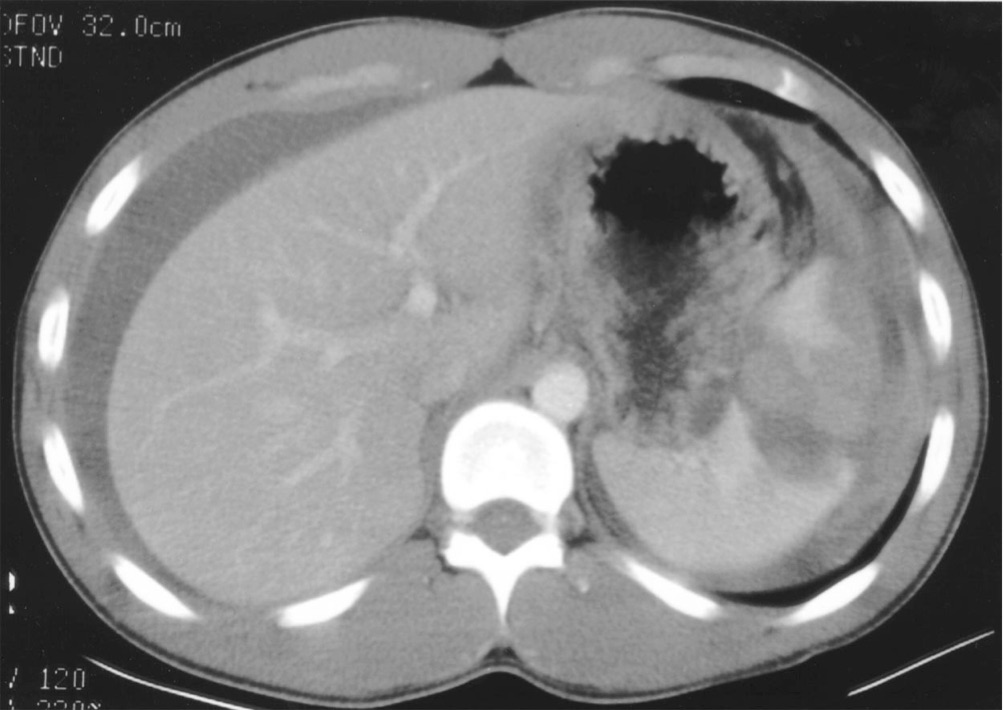
Question 4. (4 marks)
A CT scan of the patient’s abdomen is shown below. Give 2 important positive findings and 2 important negative findings?
Will you perform a CT scan of the patient? Justify your choice. (2 marks)
Question 4. (4 marks)
A CT scan of the patient’s abdomen is shown below. Give 2 important positive findings and 2 important negative findings?
saq 5.
A 77 year old woman with a prior history of a dense left CVA presents to your department with chest pain after a fall.
Her vital signs are:
HR 105 /min
BP 110/60 mmHg
RR 22 /min
Sats 94% RA
T 36.7 oC
A chest xray is ordered from triage is reproduced below.
Question 1. (5 marks)
Give 5 abnormalities seen on the X-ray.
Her vital signs are:
HR 105 /min
BP 110/60 mmHg
RR 22 /min
Sats 94% RA
T 36.7 oC
A chest xray is ordered from triage is reproduced below.
Question 1. (5 marks)
Give 5 abnormalities seen on the X-ray.
Question 2. (3 marks)
In the event of this patient becoming unstable give three problems with needle decompression of the left hemithorax.
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give 2 indications for surgical management in this patient once a large gauge chest drain is placed?
In the event of this patient becoming unstable give three problems with needle decompression of the left hemithorax.
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give 2 indications for surgical management in this patient once a large gauge chest drain is placed?