MODULE 15 short answer questions
saq 1.
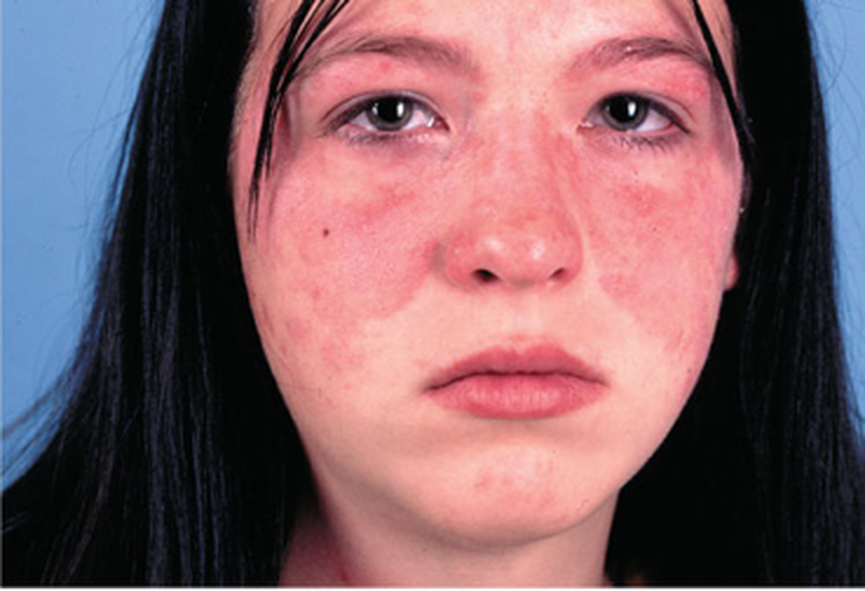
A 32 year old female presents to the emergency department complaining of fever and pain in the hands and feet. She describes increasing fatigue and 3kg of weight loss over a two month period. She has also noted a rash to her face, a picture of which is shown below.
Her vital signs are:
A clinical photo of the patient’s face is shown below.
Her vital signs are:
- HR 75 /min
- BP 110/82 mmHg
- RR 16
- Sats 96% RA
- T 37.8 oC
A clinical photo of the patient’s face is shown below.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Describe the rash.
Must include: (1 mark each)
Bilateral erythema
Largely symmetrical
Malar distribution
Patchy extension to lower cheeks and bridge of nose
Question 2. (6 marks)
Give 5 differential diagnoses, nominating your most likely diagnosis first.
Must include:
Question 3. (10 marks)
Using the table below, give 5 investigations you will order and indication for each.
Must include any of the following, which are emergency complications of lupus.
Describe the rash.
Must include: (1 mark each)
Bilateral erythema
Largely symmetrical
Malar distribution
Patchy extension to lower cheeks and bridge of nose
Question 2. (6 marks)
Give 5 differential diagnoses, nominating your most likely diagnosis first.
Must include:
- most likely diagnosis: SLE (2 marks)
- drug rash
- vasculitis
- haematological malignancy
- Stephens-Johnson syndrome
- Erythema multiforme
- Viral rash
- Erysipelas
- Lyme disease
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Scleroderma
- Sjogren’s syndrome
Question 3. (10 marks)
Using the table below, give 5 investigations you will order and indication for each.
Must include any of the following, which are emergency complications of lupus.
|
INVESTIGATION
1. ECG 2. Urine Dipstick 3. FBC 4. UEC 5. LFTs 6. CXR 7. Inflammatory markers |
COMPLICATION
1. Acute pericarditis 2. Proteinuria/haematuria (renal failure) 3. Thrombocytopaenia/leukopaenia 4. Renal failure (the most common visceral involvement of lupus) 5. Hepatitis 6. Pulmonary nodules 7. Exacerbation of disease |
saq 2.
A 4 year old girl presents with an acutely painful right hip. The child’s vital signs are:
HR 115 /min
BP 98/61 mmHg
T 37.1 oC
RR 24
Sats 99% RA
Question 1. (4 marks)
List 4 differential diagnoses.
Must include: (1 mark each)
Septic arthritis
Transient synovitis
Plus any other reasonable DDx (1 only for a maximum of 1 mark)
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 elements of the history that you will enquire about.
Must include:
Question 3. (4 marks)
List 4 investigations you may perform on this child.
Must include:
HR 115 /min
BP 98/61 mmHg
T 37.1 oC
RR 24
Sats 99% RA
Question 1. (4 marks)
List 4 differential diagnoses.
Must include: (1 mark each)
Septic arthritis
Transient synovitis
Plus any other reasonable DDx (1 only for a maximum of 1 mark)
- UTI
- Musculoskeletal injury due to trauma
- Appendicitis
- Referred pain from knee
- Perthe’s disease
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 elements of the history that you will enquire about.
Must include:
- any history of trauma and a description of same
- recent URTIs, as a risk for transient synovitis
- any infective symptoms: fever, sweats etc
- background medical and developmental history, including immunizations
Question 3. (4 marks)
List 4 investigations you may perform on this child.
Must include:
- xrays of the hip (and knee if indicated)
- FBC
- CRP
- ESR
- Ultrasound of the hip
- Urinalysis (?UTI)
saq 3.
An 81 year old female with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents after tripping and falling from standing height while gardening. She did not hit her head and there is no loss of consciousness, amnesia or vomiting. She is complaining of midline neck pain without any neurology.
Question 1. (3 marks)
Give 3 reasons this patient may be at increased risk of a c-spine injury.
Must include:
Question 2. (2 marks)
What investigation will you perform on this patient and why?
Must include:
CT scan of the neck: high risk injury, needs a sensitive investigation
Question 3. (5 marks)
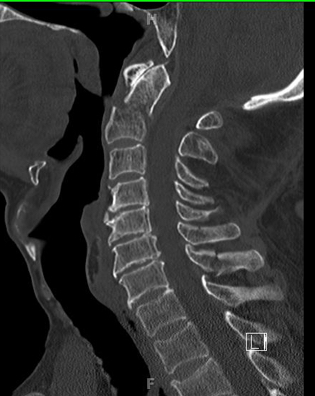
An image from the investigation you perform is shown below. Give 5 abnormalities seen.
Question 1. (3 marks)
Give 3 reasons this patient may be at increased risk of a c-spine injury.
Must include:
- rheumatoid arthritis is associated with atlanto-axial instability
- chronic steroid use as part of therapy may be associated with osteoporosis.
- Advanced age is associated with increased risk
Question 2. (2 marks)
What investigation will you perform on this patient and why?
Must include:
CT scan of the neck: high risk injury, needs a sensitive investigation
Question 3. (5 marks)
An image from the investigation you perform is shown below. Give 5 abnormalities seen.
Must include:
- fracture through base of dens
- anterior displacement of body of C2 with respect to C2
- fracture through C6 transverse process
- fracture through C7 transverse process
- significant osteoarthritic degeneration C4-C7
saq 4.
A 24 year old man presents with a painful swollen left knee of 48 hours duration. There is no history of trauma. His vital signs are:
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 4 differential diagnoses.
Must include:
Then any of:
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 2 features on history and 2 on examination that would suggest a diagnosis of reactive arthritis?
Must include:
Examination
Question 3. (2 marks)
Given your differential diagnoses, give 2 investigations will you perform on this patient to evaluate these possibilities?
Must include:
Question 4. (3 marks)
Briefly describe your procedure for arthrocentesis of the knee.
Must include the following elements:
- HR 99 /min
- BP 125/81 mmHg
- RR 16 /min
- Sats 98% RA
- Temp 37.6 oC
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 4 differential diagnoses.
Must include:
- septic arthritis
- reactive arthritis
Then any of:
- pseudogout
- gout
- seronegative spondyloarthritis (eg ankylosis spondylitis)
- or other reasonable diagnosis (NOTE fracture is NOT acceptable given stated lack of trauma)
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 2 features on history and 2 on examination that would suggest a diagnosis of reactive arthritis?
Must include:
- Hx of STD
- Symptoms of urethritis
Examination
- asymmetric oligoarthropathy
- iritis/uveitis
Question 3. (2 marks)
Given your differential diagnoses, give 2 investigations will you perform on this patient to evaluate these possibilities?
Must include:
- arthrocentesis of the knee
- urine PCR for Chlamydia
Question 4. (3 marks)
Briefly describe your procedure for arthrocentesis of the knee.
Must include the following elements:
- aseptic technique
- medial or lateral approach with knee in moderate flexion
- aspiration under the patella until synovial fluid is obtained.
SAQ 5.
A 66 year old female with a history of rheumatoid arthritis presents feeling generally unwell. She complains of some moderate abdominal pain, but has no surgical signs on examination. Her usual medications include prednisone 10mg daily and methotrexate weekly. She has no other medical history of note. Her vital signs are:
A venous blood gas is performed and the results are shown below.
pH 7.18
PO2 46 mmHg
PCO2 32 mmHg
HCO3- 16 mmol/L
Na+ 126 mmol/L
K+ 6.5 mmol/L
Cl- 105 mmol/L
Lactate 1.2 mmol/L
Question 1. (4 marks)
What are the major abnormalities on the blood gas, and what is the likely cause?
Must include:
All suggest acute adrenal insufficiency, likely due to chronic steroid use and an acute illness.
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 investigations you will perform.
Must include:
Then any of
Question 3. (4 marks)
List 4 interventions you will perform.
Must include:
Plus any other reasonable intervention
- HR 115 /min
- BP 85/68 mmHg
- RR 28 /min
- Sats 98% RA
- T 38.1 oC
A venous blood gas is performed and the results are shown below.
pH 7.18
PO2 46 mmHg
PCO2 32 mmHg
HCO3- 16 mmol/L
Na+ 126 mmol/L
K+ 6.5 mmol/L
Cl- 105 mmol/L
Lactate 1.2 mmol/L
Question 1. (4 marks)
What are the major abnormalities on the blood gas, and what is the likely cause?
Must include:
- normal anion gap metabolic acidosis
- hyponatraemia
- hyperkalaemia
All suggest acute adrenal insufficiency, likely due to chronic steroid use and an acute illness.
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 investigations you will perform.
Must include:
- urine cultures
- blood cultures
Then any of
- chest xray
- VBG lactate
- CT abdomen
Question 3. (4 marks)
List 4 interventions you will perform.
Must include:
- administration of IV hydrocortisone (or similar) 200mg
- administration of antibiotics that will cover abdominal sepsis (ceftriaxone 1g and metronidazole 500mg or amipicllin 1g, 5-7mg/kg gentamicin and metronidazole 500mg
- fluid bolus 20ml/kg aim SBP >90 or cap refill 2 secs
Plus any other reasonable intervention
- liaise with rheumatology
- administer analgesia
- administer antiemetic etc.