MODULE 19 short answer questions
saq 1.
A 45 year old female presents at 1900hrs after ingesting an unknown quantity of slow release paracetamol tablets. She is uncertain about the time of the ingestion because she is also grossly intoxicated, but a friend is able to substantiate that the overdose must have been between 1700hrs and 1830hrs.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Describe your assessment strategy for this patient.
Must include:
- assume overdose occurred as early as possible (ie 1700)
- take a four hour level at 2100
- if over treatment threshold, start NAC
- otherwise take an 8 hour level at 0100
- if over treatment threshold start NAC
- if above all OK the patient does not require treatment
Question 2. (2 marks)
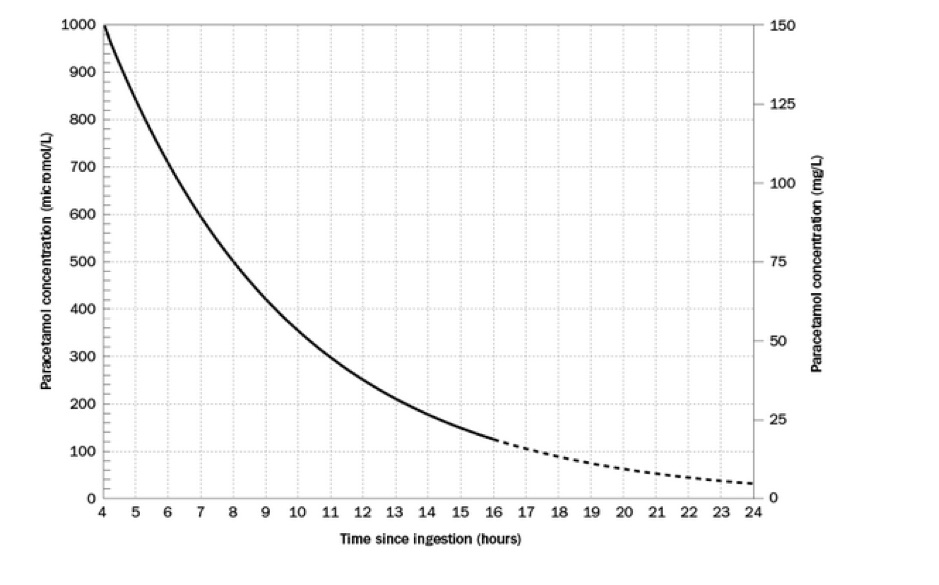
The patient’s paracetamol level at 2100hrs is 165mg/L (1100mmol/L). Interpret this result.
Must include:
- this is above the toxic level at 4 hours
- treatment with NAC should be started
The Rumack-Matthews nomogram is included below for reference. Candidates should remember 2 numbers (based on a 4hr half life of paracetamol):
1. The threshold for treatment at 4 hours is 1000mmol/L (150mg/L)
2. At 8 hours these numbers are halved to 500mmol/L and 75mg/L.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Describe your assessment strategy for this patient.
Must include:
- assume overdose occurred as early as possible (ie 1700)
- take a four hour level at 2100
- if over treatment threshold, start NAC
- otherwise take an 8 hour level at 0100
- if over treatment threshold start NAC
- if above all OK the patient does not require treatment
Question 2. (2 marks)
The patient’s paracetamol level at 2100hrs is 165mg/L (1100mmol/L). Interpret this result.
Must include:
- this is above the toxic level at 4 hours
- treatment with NAC should be started
The Rumack-Matthews nomogram is included below for reference. Candidates should remember 2 numbers (based on a 4hr half life of paracetamol):
1. The threshold for treatment at 4 hours is 1000mmol/L (150mg/L)
2. At 8 hours these numbers are halved to 500mmol/L and 75mg/L.
Question 3. (4 marks)
Describe the treatment you will institute over the next 24 hours.
Must include:
- Start NAC infusion 150mg/kg over 1hr
- followed by 50mg/kg over 4 hours
- followed by 100mg/kg over 16hrs
- referral to mental health for assessment.
Describe the treatment you will institute over the next 24 hours.
Must include:
- Start NAC infusion 150mg/kg over 1hr
- followed by 50mg/kg over 4 hours
- followed by 100mg/kg over 16hrs
- referral to mental health for assessment.
saq 2.
A 26 year old female presents with the ambulance after taking 4g of propranolol 45 minutes previously. The ambulance has placed an IVC and on arrival to the ED she has a generalized tonic clonic seizure for which she is intubated under ketamine and rocuronium. No other medications have been administered.
At this stage her vital signs are:
HR 45
BP 80/40
RR 16 (ventilated)
Sats 100% RA
GCS intubated
BSL 2.1
Question 1. (10 marks)
Give 10 interventions you will institute for this patient’s current clinical state.
Must include:
At this stage her vital signs are:
HR 45
BP 80/40
RR 16 (ventilated)
Sats 100% RA
GCS intubated
BSL 2.1
Question 1. (10 marks)
Give 10 interventions you will institute for this patient’s current clinical state.
Must include:
- Immediate administration 50ml 50% dextrose
- Administration of 1IU/kg bolus of insulin and 0.5IU/kg.hr infusion titrated to SPB 90 and HR 60 and administration of K and glucose for euglycaemia and eukalaemia (2 marks, 1 for insulin, 1 for glucose and K)
- Administration of vasopressor support
- (noradrenaline/adrenaline 10mcg/min titrated upwards)
- Administration of CaCl or CaGluconate to twice normal ionized serum calcium
- Placement of a CVC or IO to facilitate same
- Administration of 2-5mg glucagon IV bolus and infusion at the same rate per hour
- Administration of sedation to maintain intubation (morphine/midazolam, fentanyl/midazolam or ketamine infusion titrated to sedation.) NOTE as the patient is grossly hypotensive propofol is NOT an appropriate answer.
- Insertion of a NGT and administration of either activated charcoal 50g or whole bowel irrigation with colonlytely
- Insertion of an arterial line for invasive monitoring
saq 3.
A 29 year old patient presents after taking a large number of unknown tablets. On arrival he is drowsy and combative.
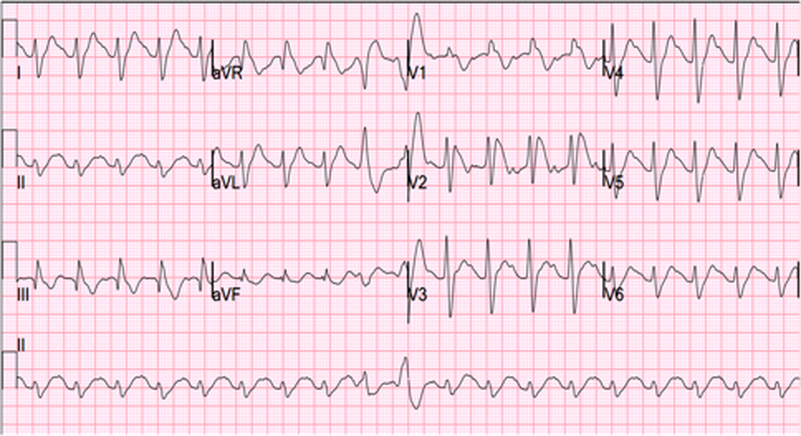
His initial ECG is shown below.
His initial ECG is shown below.
Question 1. (5 marks)
Give 5 abnormalities present on this ECG.
Must include:
Question 2. (3 marks)
Give three classes of drugs and an example of each that this patient could have taken.
Must include (0.5 marks for each drug class and 0.5 marks for an example of each):
Tricyclic antidepressants
Plus any of
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give two possible indications for the administration of sodium bicarbonate 8.4% in this patient.
Must include:
And any of
Give 5 abnormalities present on this ECG.
Must include:
- Significant tachycardia (rate ~120 BPM)
- Rightward axis
- QRS >0.12s
- Gross QT prolongation
- Large R’ in aVR
Question 2. (3 marks)
Give three classes of drugs and an example of each that this patient could have taken.
Must include (0.5 marks for each drug class and 0.5 marks for an example of each):
Tricyclic antidepressants
Plus any of
- Typical (eg haloperidol) or atypical (eg olanzapine) antipsychotics
- Type IA antiarrythmics (quinidine, procainamide) of Type 1C antiarrythmics (flecainide)
- Antihistamines (diphenhydramine)
- Antimalarials (quinine)
- Macrolides (erythromycin)
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give two possible indications for the administration of sodium bicarbonate 8.4% in this patient.
Must include:
- Prolonged QRS duration
And any of
- Cardiac arrest
- Severe dysrhythmia
- Refractory hypotension
saq 4.
An 78 year old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation presents to the emergency room complaining of dizziness and crampy abdominal pain. She gives a history of a 3 day episode of vomiting and diarrhoea, which ceased the day prior. She does not know her own medication, but mentions that she is on the “blue pills”.
Her vital signs are:
HR 38 /min
BP 98/69 mmHg
RR 24 /min
Sats 98% RA
Temp 37.3 oC
Question 1. (3 marks)
List 6 investigations you will perform.
Must include:
Then any other reasonable Ix
Question 2. (5 marks)
Selected results are shown below. Comment on the major abnormalities.
Na+ 140 mmol/L
K+ 6.7 mmol/L
Cl- 114 mmol/L
HCO3- 18 mmol/L
Urea 18.6 mmol/L
Creatinine 200 umol/L
Digoxin level 4.6 ng/mL
Must include:
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give 2 indications for the administration of digoxin-FAB fragments in this patient.
Must include:
Her vital signs are:
HR 38 /min
BP 98/69 mmHg
RR 24 /min
Sats 98% RA
Temp 37.3 oC
Question 1. (3 marks)
List 6 investigations you will perform.
Must include:
- Digoxin level
- Electrolytes and renal function
- INR
- ECG
Then any other reasonable Ix
- BSL
- FBC
- VBG and lactate etc
Question 2. (5 marks)
Selected results are shown below. Comment on the major abnormalities.
Na+ 140 mmol/L
K+ 6.7 mmol/L
Cl- 114 mmol/L
HCO3- 18 mmol/L
Urea 18.6 mmol/L
Creatinine 200 umol/L
Digoxin level 4.6 ng/mL
Must include:
- Toxic digoxin level (normal <2)
- Severe hyperkalaemia complicating this
- Elevated renal indices/acute renal failure (likely the cause of the digoxin toxicity in this instance)
- Minor drop in bicarbonate
- Normal anion gap – NAGMA likely due to renal failure
Question 3. (2 marks)
Give 2 indications for the administration of digoxin-FAB fragments in this patient.
Must include:
- Critical hypokalaemia
- Critical bradycardia
SAQ 5.
A 38 year old male with a history of bipolar disorder presents to the department feeling generally unwell. He has previously been on lithium as a mood stabilizer.
Question 1. (8 marks)
Give 8 symptoms will you ask about with respect to assessing for possible lithium toxicity?
Must include at least : (0.5 marks per Sx up to 2 marks for each category)
- CNS symptoms – tremor, parkinsonian Sx, coma, confusion
- Gastrointestinal symptoms – nausea, abdominal pain and cramps, diarrhoea, bloating
Plus any others from:
- Syncope
- Hypo/hyperthermia
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Muscle aches/weakness, syncope
Question 2. (2 marks)
Select pathology results are shown below. What are the major abnormalities?
Na+ 141 mmol/L
K+ 4.7 mmol/L
Cl- 100 mmol/L
HCO3- 23 mmol/L
Urea 16.8 mmol/L
Creatinine 170 umol/L
Lithium level 4.9 mEq/L
Must include:
- Acute renal failure
- Critically high lithium level
Question 3. (2 marks)
What immediate therapy will you institute?
Must include:
- Administration of fluid bolus (20-40ml/Kg) (to try to correct renal function)
- Referral to intensive care unit for telemetry + consideration of dialysis
Question 4. (2 marks)
What are the indications for haemodialysis in acute and chronic lithium toxicity?
Must include:
- Acute level >4.0 mEQ
- Chronic >2.5 mEQ
SAQ 6.
An 8 year old boy presents to your department with his parents who are concerned that he has been bitten by a snake while playing in the garden. A pressure immobilization bandage is currently in situ.
Question 1. (6 marks)
Give three classes of symptoms, and an example of each that you will assess this patient for.
Must include:
Question 2. (5 marks)
Give 5 investigations will you perform on this patient initially?
Must include:
Question 3.
The patient complains of some drowsiness and slurred speech. Select pathology results are shown below.
INR 6.5
APTT >200
Plt 50 x 109/L
D-Dimer 14.2 mg/dL
CK 14320 IU/L.
Give two genus of snake (common name is acceptable) that may have bitten this child?
Must include:
Question 1. (6 marks)
Give three classes of symptoms, and an example of each that you will assess this patient for.
Must include:
- Neurologic: descending paralysis, diplopia, speech/swallowing difficulties etc
- Haematologic: excessive bleeding from puncture sites, gums, haematuria, or a petechial rash
- Muscular: rhabdomolysis, muscle pain, urine colour changes.
Question 2. (5 marks)
Give 5 investigations will you perform on this patient initially?
Must include:
- CK
- Coagulation screen
- Electrolytes and renal function
- FBC/platelet count
- Urine dipstick: blood/protein
Question 3.
The patient complains of some drowsiness and slurred speech. Select pathology results are shown below.
INR 6.5
APTT >200
Plt 50 x 109/L
D-Dimer 14.2 mg/dL
CK 14320 IU/L.
Give two genus of snake (common name is acceptable) that may have bitten this child?
Must include:
- Taipan
- Tiger snake