MODULE
Below are 5 SAQs to test the application of your obstetric and general surgical knowledge. You will need a piece of paper on which to write and record your answers. You have 30 minutes. Good luck!
SAQ 1.
A 26 year old woman presents to your emergency department with cramping pain and significant vaginal bleeding. She is six weeks pregnant by dates, and this is her fourth pregnancy. Her blood pressure is 105/ 76 mmHg and heart rate is 100 bpm.
Question 1. (3 marks)
What risk factors for ectopic pregnancy will you inquire about on history?
Must include (1 mark each)
Previous ectopic pregnancy
History of tubal pathology/PID
Plus any of: (0.5 marks each up to 1 total)
Use of IUD
Use of IVF
Infertility
Multiple sexual partners
Smoking in the periconceptive period
Use of vaginal douches
Question 2. (2 marks)
What are the 2 most important blood tests you will order and why?
Must include: (0.5 mark each for reason and answer)
group and hold: check Rh status and administer antiD if necessary
bHCG titre: correlates with ultrasound sensitivity
Question 3. (2 marks)
What are the bHCG cut offs for acceptable sensitivity in detecting ectopic pregnancy for each available mode of ultrasound?
Must include:
transvaginal 1500IU/L
transabdominal 5000IU/L
Question 4. (3 marks)
The patient’s investigations return and show:
1) Quantitative bHCG 1900IU/L
2) Transvaginal ultrasound: no products of conception seen in either the uterus, fallopian tubes or abdomen. No free fluid identified.
3) G+H: AB-ve
The patient’s pain has completely settled and the bleeding has ceased. Interpret the results and outline your management including the disposition of the patient.
Must include:
bHCG above discriminatory threshold, -ve ultrasound makes it likely that this is a complete miscarriage
Rh -ve G+H indicates the administration of 125IU - 250IU of Anti-D immunoglobulin
The patient can be discharged from the ED with GP follow up.
Question 1. (3 marks)
What risk factors for ectopic pregnancy will you inquire about on history?
Must include (1 mark each)
Previous ectopic pregnancy
History of tubal pathology/PID
Plus any of: (0.5 marks each up to 1 total)
Use of IUD
Use of IVF
Infertility
Multiple sexual partners
Smoking in the periconceptive period
Use of vaginal douches
Question 2. (2 marks)
What are the 2 most important blood tests you will order and why?
Must include: (0.5 mark each for reason and answer)
group and hold: check Rh status and administer antiD if necessary
bHCG titre: correlates with ultrasound sensitivity
Question 3. (2 marks)
What are the bHCG cut offs for acceptable sensitivity in detecting ectopic pregnancy for each available mode of ultrasound?
Must include:
transvaginal 1500IU/L
transabdominal 5000IU/L
Question 4. (3 marks)
The patient’s investigations return and show:
1) Quantitative bHCG 1900IU/L
2) Transvaginal ultrasound: no products of conception seen in either the uterus, fallopian tubes or abdomen. No free fluid identified.
3) G+H: AB-ve
The patient’s pain has completely settled and the bleeding has ceased. Interpret the results and outline your management including the disposition of the patient.
Must include:
bHCG above discriminatory threshold, -ve ultrasound makes it likely that this is a complete miscarriage
Rh -ve G+H indicates the administration of 125IU - 250IU of Anti-D immunoglobulin
The patient can be discharged from the ED with GP follow up.
SAQ 2.
A 38 year old primigravida presents to your emergency department complaining of both upper and lower abdominal pain. She is 36 weeks pregnant by dates and has no medical history of note.
Her vital signs are:
BP 168/122 mmHg
HR 120 /min
RR 24 /min
O2 Sats 99% RA
T 37.2 oC
Question 1. (5 marks)
Select pathology results from blood taken at time of triage are shown below. Describe and them and outline your diagnosis/(es).
Hb 97 mg/dL
Plt 42 x109/L
AST 450 IU/L
ALT 430 IU/L
GGT 77 IU/L
ALP 66 IU/L
Must include: (3 marks, 1 for each element)
Anaemia
Thrombocytopaenia
Elevation of transaminases out of proportion to GGT and ALP
With a hypertensive primigravida these results suggest (2 marks, 1 for each diagnosis):
Pre-eclampsia
HELLP syndrome
Question 2. (4 marks)
Twenty minutes after arrival in the emergency department the patient has a generalized tonic clonic seizure. What drugs will you administer?
Must include:
MgSO4 as a 4-6g loading dose over 15-20 minutes and 2g/hr as an infusion (1 mark each for load and infusion. **must** specify doses.)
Hydralazline 5-10mg IV Q15min titrated to systolic BP of <150mmHg or diastolic BP< 90mmHg. (1 mark for dose and 1 mark for endpoints).
(Note, will accept Labetalol as an alternative to hydralzine, 20mg IV over 2 minutes plus 20mg Q10 minutes for the same endpoints.)
Question 3. (1 mark)
What is your disposition of this patient?
Must include for 1 mark:
Urgent referral to O+G for delivery of child.
Her vital signs are:
BP 168/122 mmHg
HR 120 /min
RR 24 /min
O2 Sats 99% RA
T 37.2 oC
Question 1. (5 marks)
Select pathology results from blood taken at time of triage are shown below. Describe and them and outline your diagnosis/(es).
Hb 97 mg/dL
Plt 42 x109/L
AST 450 IU/L
ALT 430 IU/L
GGT 77 IU/L
ALP 66 IU/L
Must include: (3 marks, 1 for each element)
Anaemia
Thrombocytopaenia
Elevation of transaminases out of proportion to GGT and ALP
With a hypertensive primigravida these results suggest (2 marks, 1 for each diagnosis):
Pre-eclampsia
HELLP syndrome
Question 2. (4 marks)
Twenty minutes after arrival in the emergency department the patient has a generalized tonic clonic seizure. What drugs will you administer?
Must include:
MgSO4 as a 4-6g loading dose over 15-20 minutes and 2g/hr as an infusion (1 mark each for load and infusion. **must** specify doses.)
Hydralazline 5-10mg IV Q15min titrated to systolic BP of <150mmHg or diastolic BP< 90mmHg. (1 mark for dose and 1 mark for endpoints).
(Note, will accept Labetalol as an alternative to hydralzine, 20mg IV over 2 minutes plus 20mg Q10 minutes for the same endpoints.)
Question 3. (1 mark)
What is your disposition of this patient?
Must include for 1 mark:
Urgent referral to O+G for delivery of child.
saq 3.
A 29 year old primigravida presents with a headache. She states the headache has been building up over the last 3 weeks, and that she has some peripheral visual changes. This pregnancy is currently at 35/40 and has so far been uncomplicated.
Question 1. (4 marks)
List 4 pregnancy related differentials for this patient’s presentation.
Must include:
(pre)eclampsia
dural venous sinus thrombosis
pituitary apoplexy
and either of:
vertebral artery dissection
sub arachnoid haemorrhage
Comment:
These all have an increased incidence of occurrence in pregnancy. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4380381/
(Schoen JC, Campbell RL, Sadosty AT. Headache in Pregnancy: An Approach to Emergency Department Evaluation and Management. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2015;16(2):291-301. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.1.23688.)
Question 2. (3 marks)
List 3 non radiological investigations you will perform in this patient.
Must include any 3 of
FBC
E/LFT (both for HELLP syndrome)
urine dipstick (proteinuria)
foetal HR/CTG/doppler
Question 3. (3 marks)
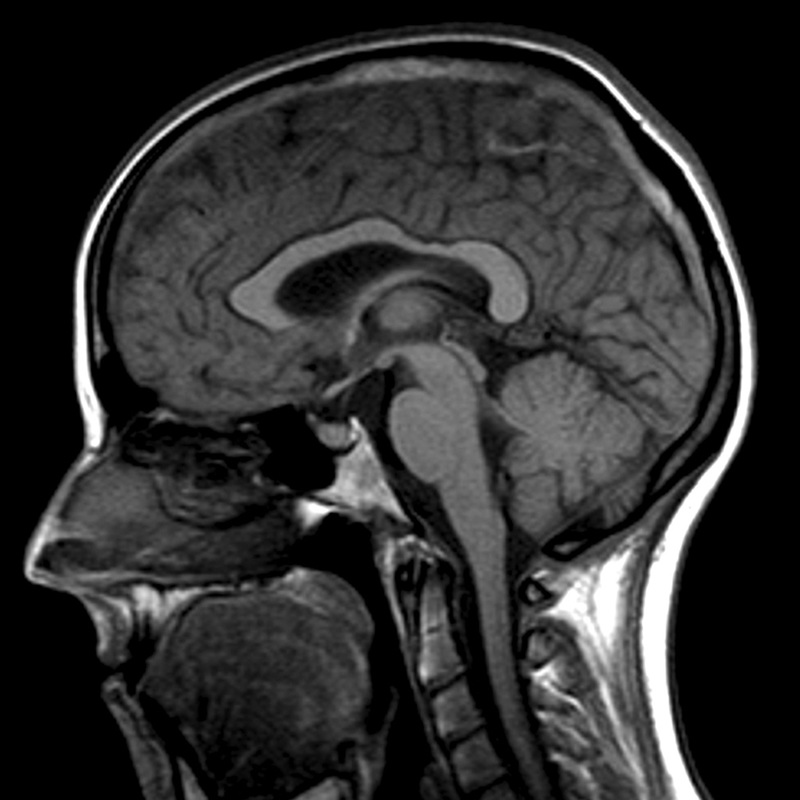
The patient has a normal blood pressure, and the investigations you have ordered are normal. An MRI scan of the patient’s brain is ordered, and a slice is shown below. What are the 2 major abnormalities and what is the diagnosis?
List 4 pregnancy related differentials for this patient’s presentation.
Must include:
(pre)eclampsia
dural venous sinus thrombosis
pituitary apoplexy
and either of:
vertebral artery dissection
sub arachnoid haemorrhage
Comment:
These all have an increased incidence of occurrence in pregnancy. See http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4380381/
(Schoen JC, Campbell RL, Sadosty AT. Headache in Pregnancy: An Approach to Emergency Department Evaluation and Management. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2015;16(2):291-301. doi:10.5811/westjem.2015.1.23688.)
Question 2. (3 marks)
List 3 non radiological investigations you will perform in this patient.
Must include any 3 of
FBC
E/LFT (both for HELLP syndrome)
urine dipstick (proteinuria)
foetal HR/CTG/doppler
Question 3. (3 marks)
The patient has a normal blood pressure, and the investigations you have ordered are normal. An MRI scan of the patient’s brain is ordered, and a slice is shown below. What are the 2 major abnormalities and what is the diagnosis?
Must include:
hyperdense sagittal sinus
hyperdense deep cerebral vein seen inferior to sagittal sinus
The diagnosis is dural venous sinus thrombosis (affecting the sagittal sinus).
hyperdense sagittal sinus
hyperdense deep cerebral vein seen inferior to sagittal sinus
The diagnosis is dural venous sinus thrombosis (affecting the sagittal sinus).
saq 4.
A 19 year old female presents to your emergency department complaining of severe abdominal cramps. She admits to being 31 weeks pregnant with her second child.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give three obstetric related features (not inclusive of vital signs) you will assess on clinical examination.
Must include:
lie of foetus
engagement of foetal head
degree of effacement and dilation of the cervix (2 marks)
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 indications for emergency delivery of this woman’s foetus.
Must include:
eclampsia
PV bleeding suggesting abruption
cord prolapse
evidence of foetal distress on CTG
Question 3. (2 marks)
There are no indications for urgent delivery, and the obstetric examination does not indicate an imminent delivery. However, she is clearly in labour. Give two medications you will administer to this patient.
Must include (note, no marks if doses not specified!):
tocolysis: nifedipine 20-60mg PO over 1 hr and then 20mg QID PO
steroids: administration of betamethasone 11.2mg
The document below is the RCOG statement on tocolysis. It’s quite long, but if you’re interested the middle part contains a discussion of the evidence for various tocolytics.
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give three obstetric related features (not inclusive of vital signs) you will assess on clinical examination.
Must include:
lie of foetus
engagement of foetal head
degree of effacement and dilation of the cervix (2 marks)
Question 2. (4 marks)
Give 4 indications for emergency delivery of this woman’s foetus.
Must include:
eclampsia
PV bleeding suggesting abruption
cord prolapse
evidence of foetal distress on CTG
Question 3. (2 marks)
There are no indications for urgent delivery, and the obstetric examination does not indicate an imminent delivery. However, she is clearly in labour. Give two medications you will administer to this patient.
Must include (note, no marks if doses not specified!):
tocolysis: nifedipine 20-60mg PO over 1 hr and then 20mg QID PO
steroids: administration of betamethasone 11.2mg
The document below is the RCOG statement on tocolysis. It’s quite long, but if you’re interested the middle part contains a discussion of the evidence for various tocolytics.
| rcog_tocolysis.pdf |
saq 5.
A 24 year old female presents to your department complaining of lower pelvic pain. The pain is severe, and localized to the right lower abdomen. She has no bowel symptoms, but does complain of some pain with urination without frequency. She also complains of some whitish vaginal discharge. Her last period was 4 weeks ago, and she says it is due in the next 2-3 days.
Her vital signs are:
HR 98 /min
BP 115/78 mmHg
RR 16 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 37.9 oC
Question 1.
What is your differential diagnosis? (3 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each)
Ectopic pregnancy
Acute appendicitis
UTI
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Plus any other reasonable 2 for 0.5 marks each up to a total of 1 mark.
Question 2.
What investigations will you perform and why? (5 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each for test and investigation)
bHCG (urine or serum): possible pregnancy
urinalysis: exclude UTI
micro for PID: either high swabs or urine PCR
plus any from: (0.5 mark for test and Ix up to maximum of 2)
ultrasound: evaluate tubo ovarian abscess or ectopic
FBC: only to evaluate Hb (possible catastrophic haemorrhage) (Note, white cell count for “infection” is not an acceptable indication)
G+H: for either suspected ectopic or blood type to evaluate need for anti-D Ig
Question 3.
On vaginal examination the patient has significant right forniceal tenderness and cervical excitation tenderness. A pregnancy test is negative. There is also some pustulent discharge visible at the cervical Os. What treatment will you administer? (2 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each)
appropriate PID schedule such as:
ceftriaxone IM or IV
metronidazole 400mg PO 14 days
azithromycin 1g stat
and repeated 1 week later OR doxycycline 100mg BD for 14 days
Her vital signs are:
HR 98 /min
BP 115/78 mmHg
RR 16 /min
Sats 99% RA
T 37.9 oC
Question 1.
What is your differential diagnosis? (3 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each)
Ectopic pregnancy
Acute appendicitis
UTI
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Plus any other reasonable 2 for 0.5 marks each up to a total of 1 mark.
Question 2.
What investigations will you perform and why? (5 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each for test and investigation)
bHCG (urine or serum): possible pregnancy
urinalysis: exclude UTI
micro for PID: either high swabs or urine PCR
plus any from: (0.5 mark for test and Ix up to maximum of 2)
ultrasound: evaluate tubo ovarian abscess or ectopic
FBC: only to evaluate Hb (possible catastrophic haemorrhage) (Note, white cell count for “infection” is not an acceptable indication)
G+H: for either suspected ectopic or blood type to evaluate need for anti-D Ig
Question 3.
On vaginal examination the patient has significant right forniceal tenderness and cervical excitation tenderness. A pregnancy test is negative. There is also some pustulent discharge visible at the cervical Os. What treatment will you administer? (2 marks)
Must include: (0.5 marks each)
appropriate PID schedule such as:
ceftriaxone IM or IV
metronidazole 400mg PO 14 days
azithromycin 1g stat
and repeated 1 week later OR doxycycline 100mg BD for 14 days