MODULE eleven short answer questions.
saq 1.
A 45 year old man presents to the emergency department after having been intubated by the retrieval service. He has poured petrol over himself and self immolated. On examination the patient has full thickness burns to the entire chest and abdomen, his entire back and circumferential burns to both upper limbs and head. You estimate a weight of 80kg.
Question 1. (2 marks)
What percentage of body surface area has been burnt? Give the underlying basis for your answer.
Question 2. (1 mark)
Is there a more accurate way to assess BSA than your estimate above?
Question 3. (3 marks)
What fluid regime will you prescribe for this patient?
Question 4. (2 marks)
Give two ways will you assess the accuracy of your fluid resuscitation.
Question 5. (1 mark)
The patient is intubated shortly after you commence your fluid resuscitation.
Post intubation you note oxygen saturations of 85%, tidal volumes of 300ml and peak airway pressures of 40cm H2O despite ventilation of 500ml SIMV and 100% O2.
What action will you now take?
Question 6. (6 marks)
Describe the procedure you will perform.
Question 1. (2 marks)
What percentage of body surface area has been burnt? Give the underlying basis for your answer.
Question 2. (1 mark)
Is there a more accurate way to assess BSA than your estimate above?
Question 3. (3 marks)
What fluid regime will you prescribe for this patient?
Question 4. (2 marks)
Give two ways will you assess the accuracy of your fluid resuscitation.
Question 5. (1 mark)
The patient is intubated shortly after you commence your fluid resuscitation.
Post intubation you note oxygen saturations of 85%, tidal volumes of 300ml and peak airway pressures of 40cm H2O despite ventilation of 500ml SIMV and 100% O2.
What action will you now take?
Question 6. (6 marks)
Describe the procedure you will perform.
saq 2.
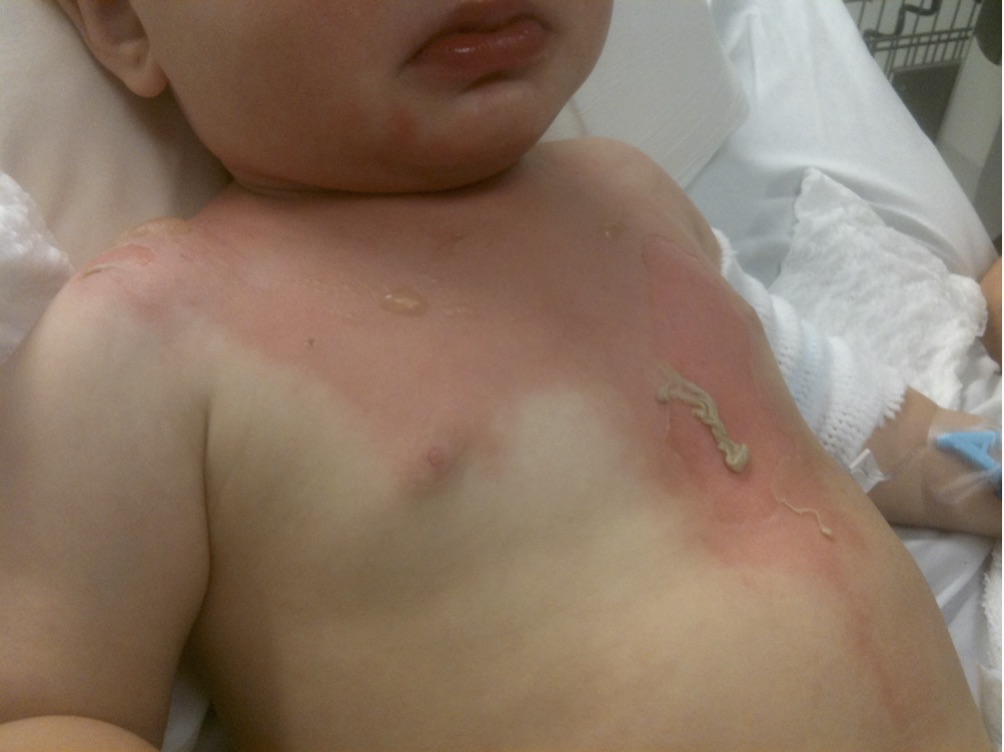
A 2 year old child presents to the ED with his mother after pulling a bowl of hot noodles down onto himself. A clinical image of the child is shown below.
Question 1. (2 marks)
Give 2 important features of the photo:
Question 2. (1 mark)
What are the likely depth of these burns?
Question 3. (3 marks)
Give 3 important steps in your initial management.
Question 4. (4 marks)
Fill in the following table to indicate the type of tetanus prophylaxis required for immunized and non immunized patients who receive tetanus prone wounds.
Give 2 important features of the photo:
Question 2. (1 mark)
What are the likely depth of these burns?
Question 3. (3 marks)
Give 3 important steps in your initial management.
Question 4. (4 marks)
Fill in the following table to indicate the type of tetanus prophylaxis required for immunized and non immunized patients who receive tetanus prone wounds.
|
TETANUS RISK
LOW HIGH |
UNIMMUNIZED
|
IMMUNIZED
|
saq 3.
A 45 year old electrician presents to the emergency department after receiving an electric shock at work from a 240V AC mains outlet. He touched an extension cord that had exposed wire, and received a shock which jolted him backwards.
Question 1. (3 marks)
Give three features will you look for on examination?
Question 2. (2 marks)
The patient subsequently has a normal physical examination. Which investigation will you perform and why?
Question 3. (5 marks)
Fill in the following table for patterns of injury associated with electrical injury.
Question 1. (3 marks)
Give three features will you look for on examination?
Question 2. (2 marks)
The patient subsequently has a normal physical examination. Which investigation will you perform and why?
Question 3. (5 marks)
Fill in the following table for patterns of injury associated with electrical injury.
|
VOLTAGE
Low (<1000 volts) High (>1000 volts) Lightning Strike |
EXAMPLE OF EXPOSURE
|
PATTERNS OF INJURY
|
saq 4.
A 75 year old woman presents after falling on her outstretched right arm. She is right hand dominant and normally lives independently. The arm is significantly deformed, but she has no other injuries. Her medical history includes a NSTEMI 6 months prior, as well as COPD which limits her exercise tolerance to 100m.
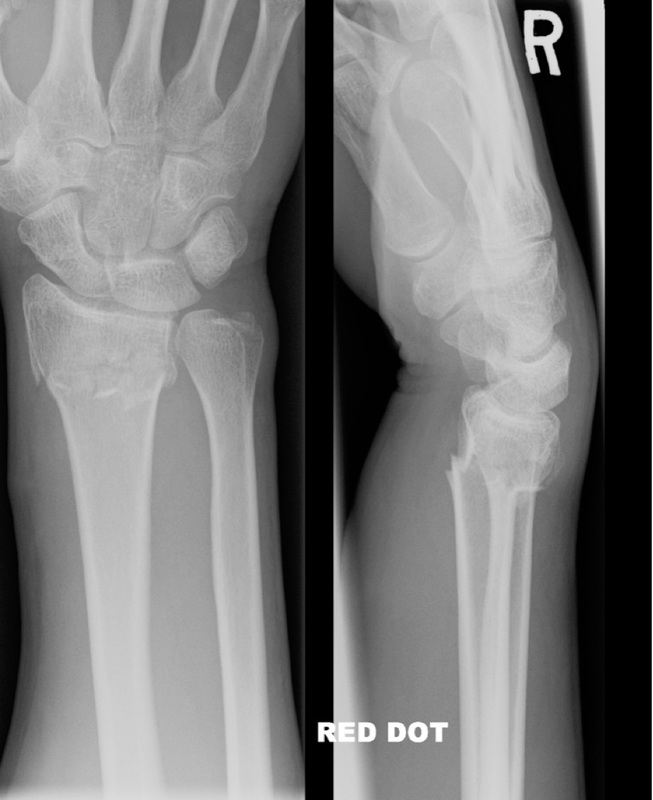
Plain radiographs of the forearm are shown below.
Plain radiographs of the forearm are shown below.
Question 1. (2 marks)
Describe 2 major findings on the xray.
Question 2. (2 marks)
Your registrar asks you to provide sedation so that the fracture can be reduced in ED. What is your response?
Question 3. (8 marks)
Discuss four safe management strategies for this patient’s fracture using the format below.
Describe 2 major findings on the xray.
Question 2. (2 marks)
Your registrar asks you to provide sedation so that the fracture can be reduced in ED. What is your response?
Question 3. (8 marks)
Discuss four safe management strategies for this patient’s fracture using the format below.
|
STRATEGY
1. 2. 3. 4. |
PRO
|
CON
|
SAQ 5.
A 31 year old male is brought in by the ambulance after being struck by a car whilst crossing the street. Bystanders report that the car struck him directly in the waist.
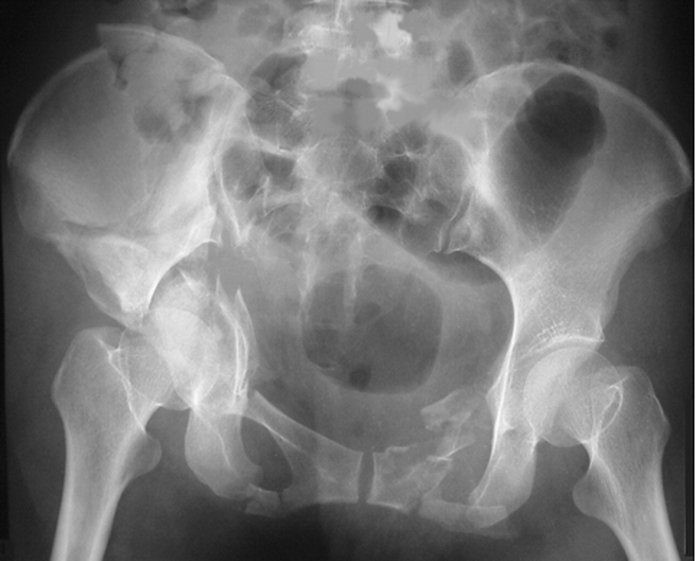
A trauma xray is shown below.
A trauma xray is shown below.
Question 1 (4 marks).
Give 4 major abnormalities seen on the xray.
Question 2. (3 marks)
What features on clinical examination will make you suspect a urethral injury?
Question 3. (3 marks)
After CT "pan scanning" no other injuries are identified. After 4 units of blood the patient's blood pressure is 92/60mmHg and his HR is 114/min. The orthopaedic registrar has some doubt over the disposition of this patient. What will you tell her?
Give 4 major abnormalities seen on the xray.
Question 2. (3 marks)
What features on clinical examination will make you suspect a urethral injury?
Question 3. (3 marks)
After CT "pan scanning" no other injuries are identified. After 4 units of blood the patient's blood pressure is 92/60mmHg and his HR is 114/min. The orthopaedic registrar has some doubt over the disposition of this patient. What will you tell her?
SAQ 5
A 32 year old woman who is 24 weeks pregnant is brought into the emergency department by ambulance. She was a passenger in a high speed motor vehicle accident. She has no other relevant past history.
She has sustained a head injury with an episode of loss of consciousness. She has a small scalp laceration and has right lateral chest wall tenderness to palpation.
1. Complete below indicating which parameter increases or decreases in pregnancyMaternal Heart rate: _________________________________________________________
Maternal Blood volume: _____________________________________________________
Maternal white cell count:___________________________________________________
Maternal CO2:______________________________________________________________
Maternal Functional residual capacity:______________________________________
Maternal rate of gastric emptying: _________________________________________
2. You decide to perform an eFAST examination. The abdomen looks normal, however you are concerned about a potential pneumothorax on ultrasound. You speak to the patient about performing a CXR to look for a pneumothorax. The patient is concerned about radiation exposure of the fetus.
(a) What is considered a safe level of exposure during pregnancy?
(b) What is the exposure of a:
i.CXR? ___________________________________________________
ii.Pelvic XRay? ______________________________________________
iii.CT Brain? ________________________________________________
iv.CT abdomen? _____________________________________________
3 You perform a CXR which shows a large right sided pneumothorax and 3 fractured ribs. You decide to insert a chest tube. Please briefly outline the position of insertion of the tube as it relates to the obstetric patient.
4 You decide to monitor with cardiotocography
(a) How long should you monitor a patient for?
(b) List the specific information you are looking
-List one thing you are looking for in the mother
-List 3 things you look for in terms of the fetal heart rate
5 List 3 ways in which placental abruption can present.
She has sustained a head injury with an episode of loss of consciousness. She has a small scalp laceration and has right lateral chest wall tenderness to palpation.
1. Complete below indicating which parameter increases or decreases in pregnancyMaternal Heart rate: _________________________________________________________
Maternal Blood volume: _____________________________________________________
Maternal white cell count:___________________________________________________
Maternal CO2:______________________________________________________________
Maternal Functional residual capacity:______________________________________
Maternal rate of gastric emptying: _________________________________________
2. You decide to perform an eFAST examination. The abdomen looks normal, however you are concerned about a potential pneumothorax on ultrasound. You speak to the patient about performing a CXR to look for a pneumothorax. The patient is concerned about radiation exposure of the fetus.
(a) What is considered a safe level of exposure during pregnancy?
(b) What is the exposure of a:
i.CXR? ___________________________________________________
ii.Pelvic XRay? ______________________________________________
iii.CT Brain? ________________________________________________
iv.CT abdomen? _____________________________________________
3 You perform a CXR which shows a large right sided pneumothorax and 3 fractured ribs. You decide to insert a chest tube. Please briefly outline the position of insertion of the tube as it relates to the obstetric patient.
4 You decide to monitor with cardiotocography
(a) How long should you monitor a patient for?
(b) List the specific information you are looking
-List one thing you are looking for in the mother
-List 3 things you look for in terms of the fetal heart rate
5 List 3 ways in which placental abruption can present.