MODULE eleven short answer questions.
saq 1.
A 55 year old man presents to your emergency department with sudden onset central crushing chest pain.
His vital signs are:
HR 60 /min
BP 108/55 mmHg
RR 28 /min
Sats 92% 6L
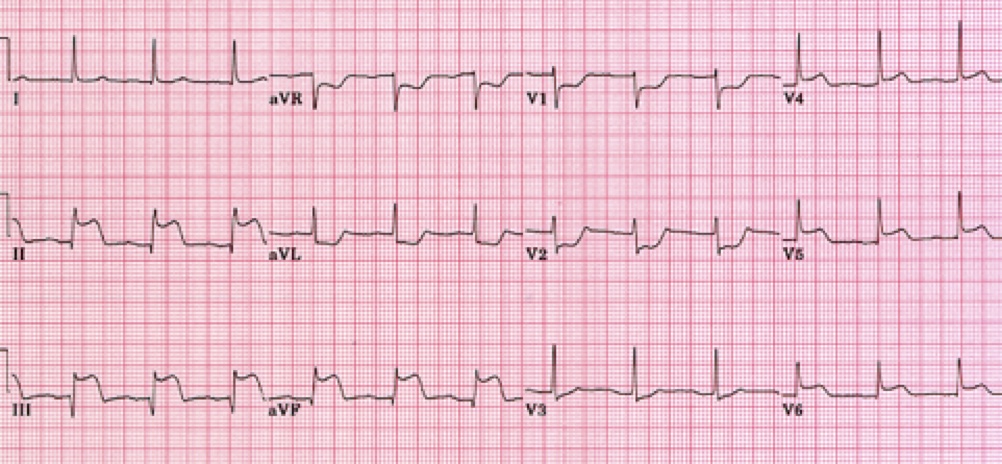
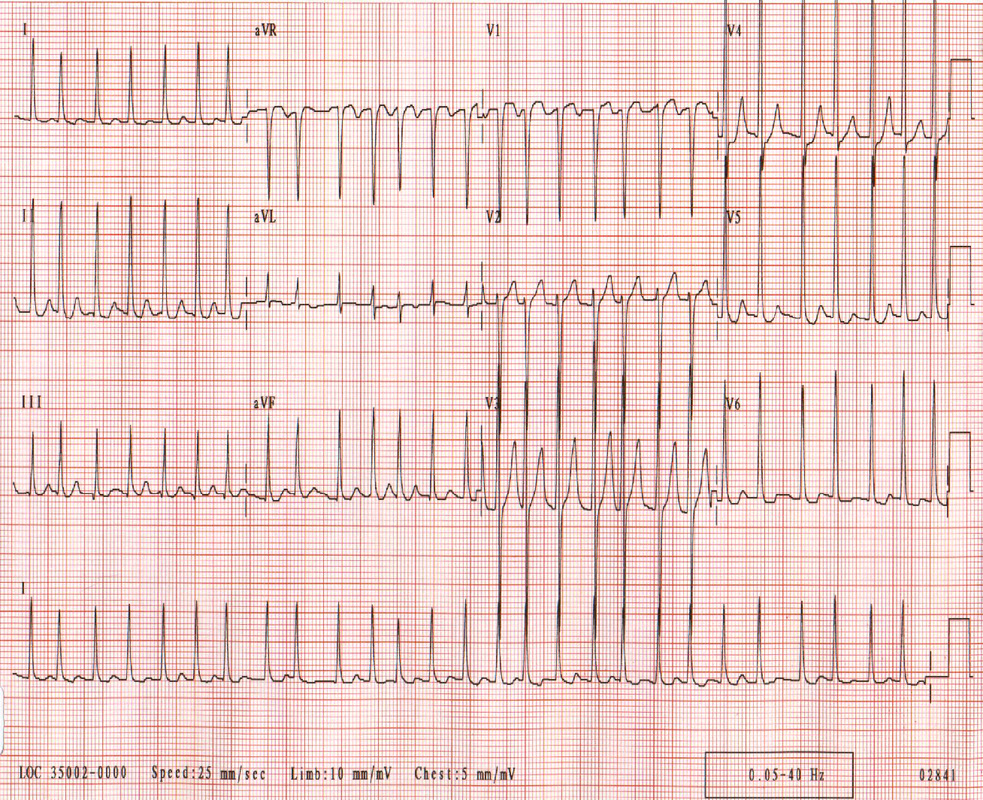
His ECG on presentation is shown below.
His vital signs are:
HR 60 /min
BP 108/55 mmHg
RR 28 /min
Sats 92% 6L
His ECG on presentation is shown below.
Question 1. (3 marks)
Give 3 major abnormalities shown on the ECG.
Must include:
~5mm ST elevation inferiorly (II, II & aVF)
~2mm ST elevation V4 - V6
reciprocal depression aVR, aVL, V1 & V2
Question 2. (2 marks)
What is the diagnosis?
Must include:
Infero-lateral STEMI
Question 3. (4 marks)
Which is the most likely artery affected, and why?
Must include:
Circumflex artery
Question 4. (1 mark)
What other ECG will you perform on this patient?
Must include R sided ECG
Give 3 major abnormalities shown on the ECG.
Must include:
~5mm ST elevation inferiorly (II, II & aVF)
~2mm ST elevation V4 - V6
reciprocal depression aVR, aVL, V1 & V2
Question 2. (2 marks)
What is the diagnosis?
Must include:
Infero-lateral STEMI
Question 3. (4 marks)
Which is the most likely artery affected, and why?
Must include:
Circumflex artery
- suggested by equal elevation in lead II & III,
- presence of lateral infarction
- the absence of reciprocal depression in I.
Question 4. (1 mark)
What other ECG will you perform on this patient?
Must include R sided ECG
saq 2.
A 66 year old female presents to your department with acute central crushing chest pain of 2 hours duration.
Her vital signs are:
HR 48 /min
BP 69/45 mmHg
RR 32 /min
Sats 92% 6L
Her vital signs are:
HR 48 /min
BP 69/45 mmHg
RR 32 /min
Sats 92% 6L
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 4 major abnormalities from the ECG?
Must include:
ST elevation in III, II & aVF, greatest in lead three
Deep ST depression in I and aVL
Complete heart block (dissociation of p and qrs complexes)
Borderline ST elevation in aVR
Question 2. (2 marks)
Where is the anatomical lesion?
Most likely R coronary artery given asymmetry of inferior elevation (greatest in III), lack of lateral ST elevation, and deep TWI in I and aVL.
Question 3. (2 marks)
What further ECG investigations will you perform and why?
Must include:
Question 4. (2 marks)
Why is this test important for management?
Hypotensive R sided infarcts are treated with an increase in preload (IV fluid) and avoidance of GTN (which decreases preload).
Give 4 major abnormalities from the ECG?
Must include:
ST elevation in III, II & aVF, greatest in lead three
Deep ST depression in I and aVL
Complete heart block (dissociation of p and qrs complexes)
Borderline ST elevation in aVR
Question 2. (2 marks)
Where is the anatomical lesion?
Most likely R coronary artery given asymmetry of inferior elevation (greatest in III), lack of lateral ST elevation, and deep TWI in I and aVL.
Question 3. (2 marks)
What further ECG investigations will you perform and why?
Must include:
- right sided ECG to assess for the possibility of right sided STEMI
Question 4. (2 marks)
Why is this test important for management?
Hypotensive R sided infarcts are treated with an increase in preload (IV fluid) and avoidance of GTN (which decreases preload).
saq 3.
A 48 year old male presents with acute chest pain of 90 minutes duration. An ECG is performed on arrival and shows an anterior STEMI.
Question 1. (3 marks)
What is your preferred repercussion strategy and why?
Must include:
Question 2. (3 marks)
The cardiology lab phones you to tell you there will be a 60 minute delay to the patient being transferred. Does this change your repercussion strategy?
Must include:
Question 3. (5 marks)
A further delay of 60 minutes is anticipated. Describe your subsequent management of the patient.
Must include:
Question 1. (3 marks)
What is your preferred repercussion strategy and why?
Must include:
- emergent PCI
- more likely to establish TIMI grade 3 flow
- clear mortality benefit in anterior STEMI over lysis (2.8 vs 10%) as well as post-infarct angina, 6 month mortality etc.
Question 2. (3 marks)
The cardiology lab phones you to tell you there will be a 60 minute delay to the patient being transferred. Does this change your repercussion strategy?
Must include:
- NO
- benefit of PCI over lysis extends to a period of 90-120 minutes after 1st medical contact. Thus only after a period of 90 minutes should lysis be considered over PCI.
Question 3. (5 marks)
A further delay of 60 minutes is anticipated. Describe your subsequent management of the patient.
Must include:
- thrombolysis indicated at this stage
- administer aspirin 300mg & antiplatelet agent (eg clopidogrel 300-600mg)
- administer heparin pre-lysis: enoxaparin 30mg IV
- administration of tPA based on weight
- administration of s/c heparin post lysis: 1mg/kg enoxaparin
saq 4.
A 55 year old male presents to your ED with new onset central chest pain that occurred by walking up a hill. The pain was relieved by GTN and aspirin with the ambulance service.
He has no medical history of note, and takes no medications.
Question 1. (2 marks)
Give 2 further ACS high risk features you will look for as part of your workup.
Must include:
Question 2. (3 marks)
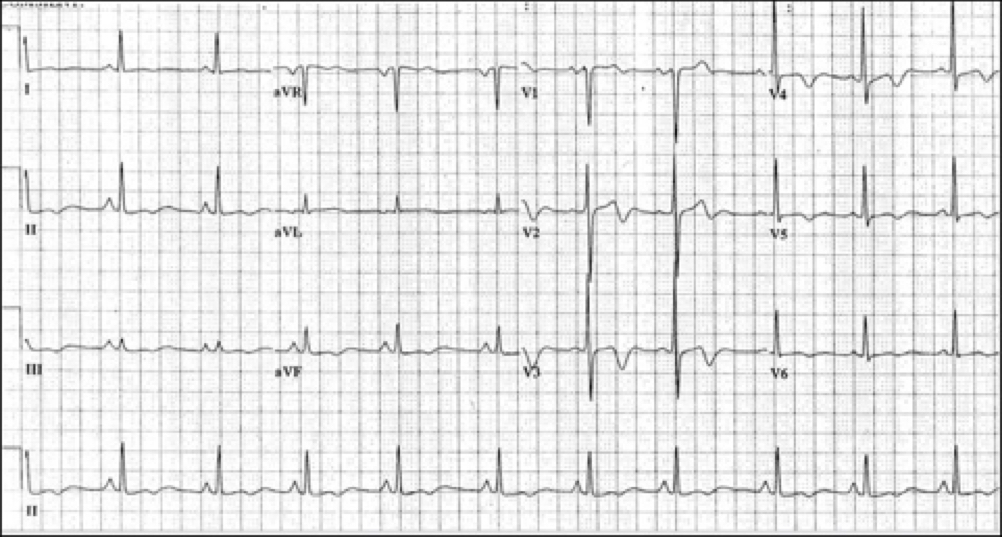
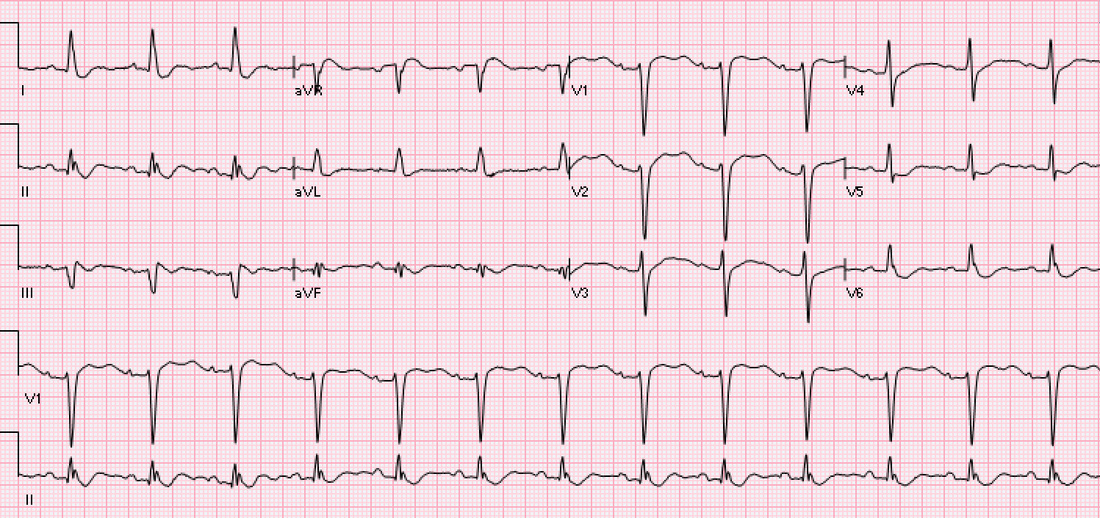
The patient’s ECG is shown below. What is the major abnormality and what is the diagnosis?
He has no medical history of note, and takes no medications.
Question 1. (2 marks)
Give 2 further ACS high risk features you will look for as part of your workup.
Must include:
- Presence of ECG changes
- Positive biomarkers (troponin)
Question 2. (3 marks)
The patient’s ECG is shown below. What is the major abnormality and what is the diagnosis?
Must include:
Deep biphasic t waves in V2 - V4 (1 mark)
which indicates Wellen’s syndrome (critical LAD stenosis). (2 marks)
Question 3. (5 marks)
Your resident advises you the cardiology registrar has reviewed this patient, and plans to perform a stress test if serial troponin are negative at 6 hours. Describe your response.
Must include:
Deep biphasic t waves in V2 - V4 (1 mark)
which indicates Wellen’s syndrome (critical LAD stenosis). (2 marks)
Question 3. (5 marks)
Your resident advises you the cardiology registrar has reviewed this patient, and plans to perform a stress test if serial troponin are negative at 6 hours. Describe your response.
Must include:
- recognition that this patient has a high risk for coronary artery disease and death, and that a stress test may precipitate an acute MI
- therefore the management plan is inappropriate, and should be revised with the cardiology registrar to ensure an angiogram is performed.
- if necessary this should be escalated by discussion directly between the FACEM and the cardiologist
SAQ 5.
A 31 year old man on dialysis for end stage glomerulonephritis presents with central chest pain. He missed his dialysis 2 days ago.
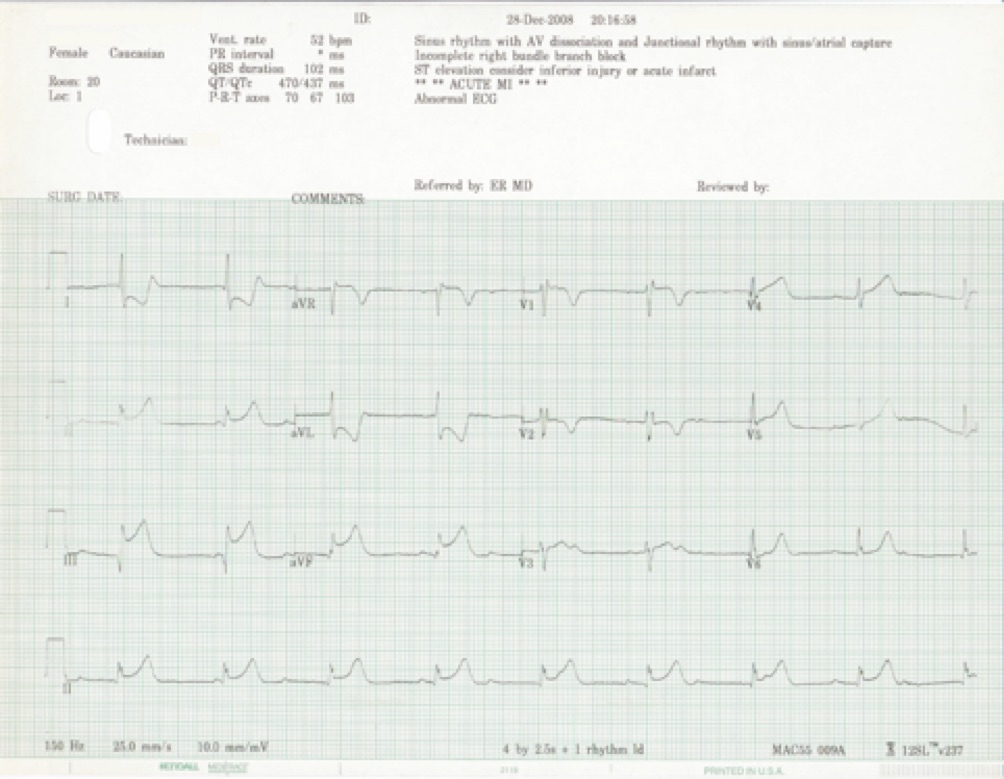
An ECG on arrival is shown below.
Question 1. (3 marks)
What are the major abnormalities and what is the likely diagnosis?
An ECG on arrival is shown below.
Question 1. (3 marks)
What are the major abnormalities and what is the likely diagnosis?
Must include:
Diagnosis: acute pericarditis.
Question 2. (5 marks)
Give 5 features on history and examination will you seek to would support this diagnosis?
Must include:
Examination
Note, there are a variety of other signs and symptoms candidates might wish to suggest via the VSG.
Question 3. (2 marks)
The patient's urea and electrolyte profile returns.
Give 4 major abnormalities present.
Na+ 142 mmol/L
K+ 5.8 mmol/L
Cl- 102 mmol/L
HCO3- 15 mmol/L
Urea 38 mmol/L
Creatinine 780 umol/L
Must include:
Raised anion gap metabolic acidosis/low bicarbonate
critically elevated renal indices (urea and creatinine)
mild-moderate hyperkalaemia
Question 4. (2 marks)
Give two management steps you will institute for this patient.
Must include:
Note as there are no ECG changes of hyperkalaemia acute treatment of hyperkalaemia scores NO marks, nor does the administration of IV fluids to this dialysis patient)
- diffuse/non-anatomical ST elevation in leads I, II, aVF, AVL, and V2 - V6
- saddle shaped ST segments
Diagnosis: acute pericarditis.
Question 2. (5 marks)
Give 5 features on history and examination will you seek to would support this diagnosis?
Must include:
- stabbing/knifelike pain
- pain worse with lying flat and swallowing
- pain improved by sitting forwards
- pain located retrosternally
Examination
- presence of a pericardial friction rub.
Note, there are a variety of other signs and symptoms candidates might wish to suggest via the VSG.
Question 3. (2 marks)
The patient's urea and electrolyte profile returns.
Give 4 major abnormalities present.
Na+ 142 mmol/L
K+ 5.8 mmol/L
Cl- 102 mmol/L
HCO3- 15 mmol/L
Urea 38 mmol/L
Creatinine 780 umol/L
Must include:
Raised anion gap metabolic acidosis/low bicarbonate
critically elevated renal indices (urea and creatinine)
mild-moderate hyperkalaemia
Question 4. (2 marks)
Give two management steps you will institute for this patient.
Must include:
- administration of analgesia (paracetamol or NSAID)
- referral for dialysis
Note as there are no ECG changes of hyperkalaemia acute treatment of hyperkalaemia scores NO marks, nor does the administration of IV fluids to this dialysis patient)
SAQ 6.
A 72 year old lady with a history of diabetes presents complaining of frequency of urine and dysuria. She takes metformin 500mg BD for her diabetes but has no other medical history or medication use.
Her vital signs are:
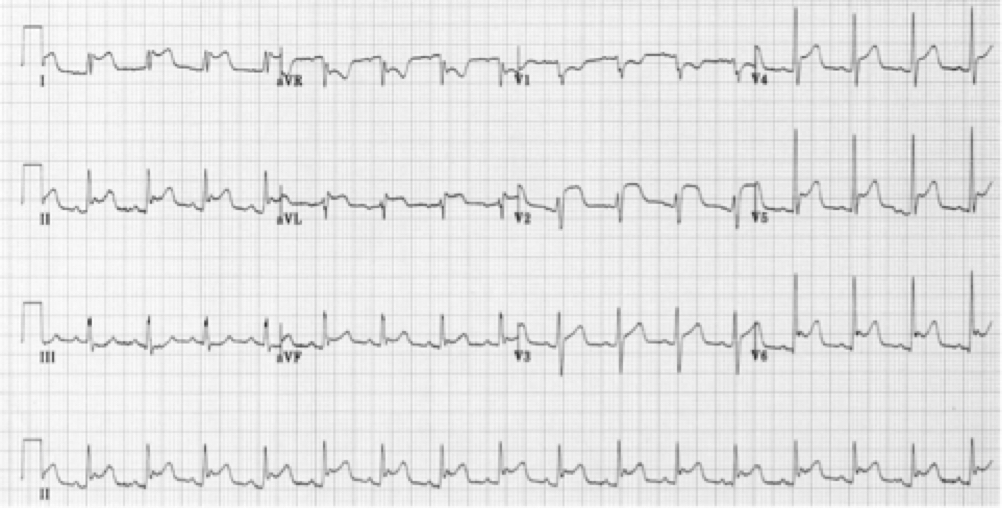
Her ECG taken as part of her initial work up is shown below.
Question 1. (5 marks)
Describe the ECG and give a diagnosis.
Her vital signs are:
- HR 145/min
- BP 86/40 mmHg
- RR 28 /min
- Sats 99% RA
- T 39.6 oC
Her ECG taken as part of her initial work up is shown below.
Question 1. (5 marks)
Describe the ECG and give a diagnosis.
Must include:
- rate 168bpm
- irregular rhythm
- absent P waves
- narrow complex QRS
diagnosis: atrial fibrillation
Question 2. (8 marks)
The patient's electrolyte profile is shown below.
Give 4 interventions you will apply to this patient, including any endpoints you would use.
Na+ 141 mmol/L
K+ 2.8 mmol/L
Cl- 102 mmol/L
HCO3- 19 mmol/L
Ca++ 2.25 mmol/L
Mg++ 0.5 mmol/L
Urea 5.8 mmol/L
Creatinine 70 umol/L
Must include:
1. Administration of fluid bolus 20-40ml/Kg aiming HR 100 SBP >90
2. Replace K+ administer 10mmol/l KCl over 30 mins repeat >4.5mmol/L
3. Replace Mg++ administer 10mmol MgSO4 over 30mins repeat Mg 1.0
4. Treat for UTI/urosepsis: ceftriaxone 1g STAT, plus gentamicin 5-7mg/kg
Note - this patient has AF, but is also septic. Don't forget managing the sepsis as part of your answer!
Question 3. (4 marks)
After your initial treatment the patient remains hypotensive with the same heart rhythm. A decision is taken to cardiovert the patient.
Describe your procedure for this.
Must include:
- use of pads and leads simultaneously
- synchronisation of defibrillator
- administration of an appropriate dose of sedation (fentanyl 0.5mcg/kg IV and midazolam 1-2mg)
- 200J synchronized shock
- rate 168bpm
- irregular rhythm
- absent P waves
- narrow complex QRS
diagnosis: atrial fibrillation
Question 2. (8 marks)
The patient's electrolyte profile is shown below.
Give 4 interventions you will apply to this patient, including any endpoints you would use.
Na+ 141 mmol/L
K+ 2.8 mmol/L
Cl- 102 mmol/L
HCO3- 19 mmol/L
Ca++ 2.25 mmol/L
Mg++ 0.5 mmol/L
Urea 5.8 mmol/L
Creatinine 70 umol/L
Must include:
1. Administration of fluid bolus 20-40ml/Kg aiming HR 100 SBP >90
2. Replace K+ administer 10mmol/l KCl over 30 mins repeat >4.5mmol/L
3. Replace Mg++ administer 10mmol MgSO4 over 30mins repeat Mg 1.0
4. Treat for UTI/urosepsis: ceftriaxone 1g STAT, plus gentamicin 5-7mg/kg
Note - this patient has AF, but is also septic. Don't forget managing the sepsis as part of your answer!
Question 3. (4 marks)
After your initial treatment the patient remains hypotensive with the same heart rhythm. A decision is taken to cardiovert the patient.
Describe your procedure for this.
Must include:
- use of pads and leads simultaneously
- synchronisation of defibrillator
- administration of an appropriate dose of sedation (fentanyl 0.5mcg/kg IV and midazolam 1-2mg)
- 200J synchronized shock
SAQ 7.
Your registrar calls you to resus to see a patient he is concerned about. A 50 year old man has presented with 3 days of profuse vomiting, and is moderately dehydrated. Your registrar mentions that intravenous access was extremely difficult, but he has successfully sent bloods. The patient's vital signs are:
pH 7.58
PCO2 45 mmHg
HCO3- 28 mmol/L
Na+ 138 mmol/L
K+ 5.8 mmol/L
Cl- 72 mmol/L
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 4 abnormalities seen on the blood gas.
Must include:
- metabolic alkalosis
- respiratory compensation
- mild - moderate hyperkalaemia
- profound hypochloraemia
Question 2. (1 mark)
What is the likely aetiology of the primary acid-base disturbance?
Must include:
- metabolic alkalosis due to excessive HCl loss (vomiting)
Question 3. (2 marks)
The patient has an ECG taken.
Give 2 abnormalities seen on the ECG.
- HR 110/min
- BP 99/60 mmHg
- RR 12 /min
- Sats 99% RA
- T 37.3 oC
pH 7.58
PCO2 45 mmHg
HCO3- 28 mmol/L
Na+ 138 mmol/L
K+ 5.8 mmol/L
Cl- 72 mmol/L
Question 1. (4 marks)
Give 4 abnormalities seen on the blood gas.
Must include:
- metabolic alkalosis
- respiratory compensation
- mild - moderate hyperkalaemia
- profound hypochloraemia
Question 2. (1 mark)
What is the likely aetiology of the primary acid-base disturbance?
Must include:
- metabolic alkalosis due to excessive HCl loss (vomiting)
Question 3. (2 marks)
The patient has an ECG taken.
Give 2 abnormalities seen on the ECG.
Must include:
- presence of U waves/flattening of t waves
- borderline PR prolongation or other reasonable comment
Question 4. (2 marks)
What electrolyte abnormality is the ECG most consistent with, and how does this fit with the patient's presentation?
Must include:
- hypokalaemia
- this is discrepant with the measured K+ most likely due to haemolysis (difficult vascular access)
Question 5. (3 marks)
Give 3 actions you will undertake for this patient in resus.
Fluid bolus 20ml/Kg aiming HR 100, SBP >90 and cap refill 2 secs
Place patient on telemetry
Recheck K+ and replace if confirmed low
Note, treatment of hyperkalaemia with insulin etc is a critical failure and will result in 0 marks for the entire SAQ.
- presence of U waves/flattening of t waves
- borderline PR prolongation or other reasonable comment
Question 4. (2 marks)
What electrolyte abnormality is the ECG most consistent with, and how does this fit with the patient's presentation?
Must include:
- hypokalaemia
- this is discrepant with the measured K+ most likely due to haemolysis (difficult vascular access)
Question 5. (3 marks)
Give 3 actions you will undertake for this patient in resus.
Fluid bolus 20ml/Kg aiming HR 100, SBP >90 and cap refill 2 secs
Place patient on telemetry
Recheck K+ and replace if confirmed low
Note, treatment of hyperkalaemia with insulin etc is a critical failure and will result in 0 marks for the entire SAQ.